What Is Physical Literacy?
Most of us are familiar with the term language literacy. It means we are able to use our language actively and passively in a variety of ways including reading, writing, and speaking. Similarly, the term physical literacy means that we are able to move our bodies with competence and confidence in a wide variety of physical activities across multiple environments.

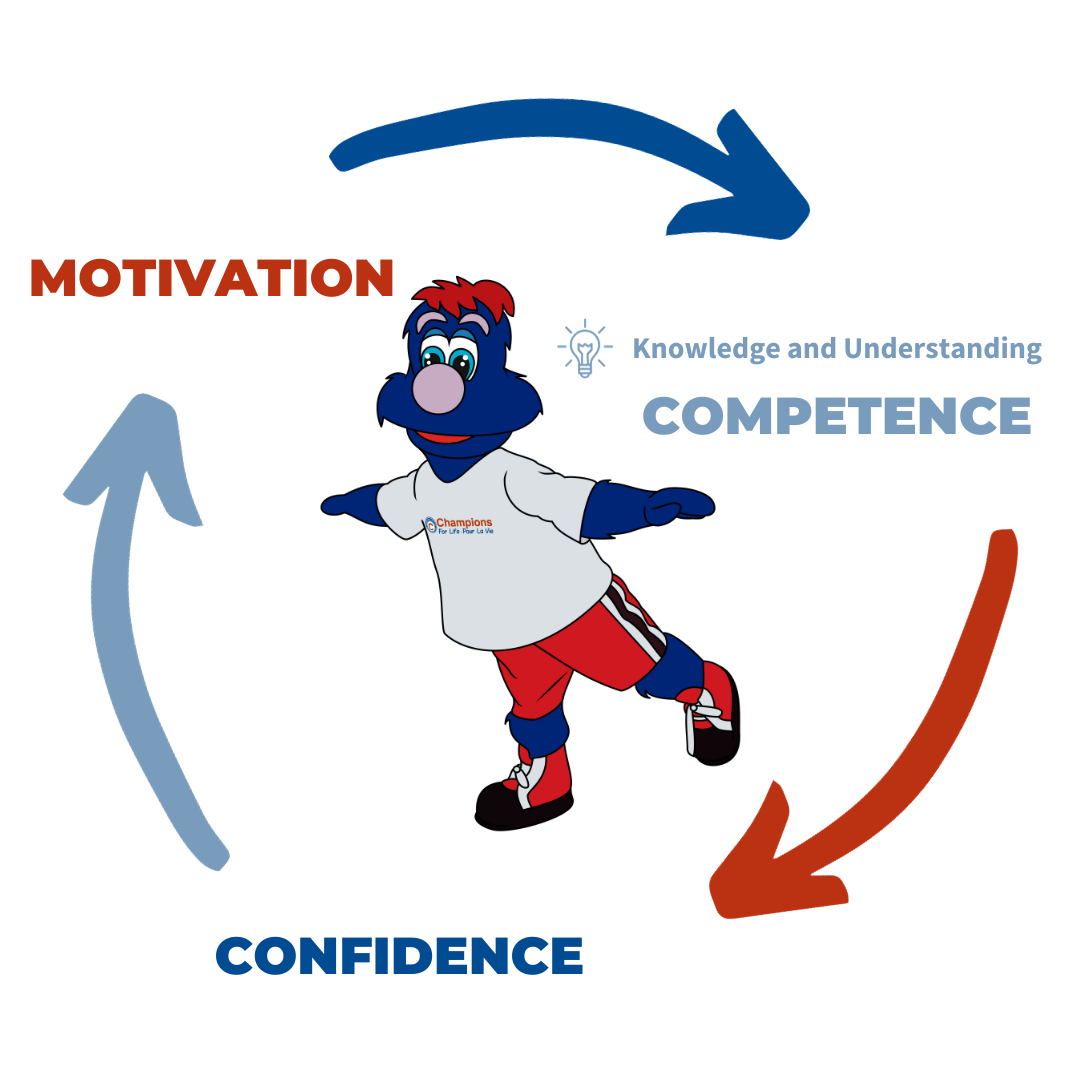
Physical literacy is the motivation, confidence, physical competence, knowledge, and understanding to value and take responsibility for engagement in physical activities for life.
International Physical Literacy Association, 2014

Why Is Physical Literacy Important?
Physical literacy is an important building block which supports children to be active. Without basic skills, children often become disengaged from sport and activity.
The benefits of physical literacy aren’t limited to physical health. We also know that kids who are more active also have improved academic performance, cognitive skills, mental wellness, social skills and healthy lifestyle habits.
The Three Core Elements of Physical Literacy
The Five Core Components of Physical Literacy
How Is Physical Literacy Different from Physical Activity?
Physical Activity is how you move and the energy you use while moving. In contrast, Physical Literacy is the development of fundamental movement skills that allow you to participate in various physical activities. These factors are connected as our physical literacy affects our participation in physical activities and our commitment to being active for life.
What are fundamental movement skills?
Fundamental Movement Skills (FMS) are the building blocks of Physical Literacy and can be organized into three categories: Balance, Locomotion, and Object Manipulation Skills. FMS help children read their environment, make appropriate decisions, and move confidently and with control in various physical activity situations.